augmenters.size¶
Resize¶
Augmenter that resizes images to specified heights and widths.
API link: Resize
Example. Resize each image to height=32 and width=64:
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.Resize({"height": 32, "width": 64})

Example. Resize each image to height=32 and keep the aspect ratio for width the same:
aug = iaa.Resize({"height": 32, "width": "keep-aspect-ratio"})

Example. Resize each image to something between 50 and 100% of its original size:
aug = iaa.Resize((0.5, 1.0))

Example. Resize each image’s height to 50-75% of its original size and width to either 16px or 32px or 64px:
aug = iaa.Resize({"height": (0.5, 0.75), "width": [16, 32, 64]})

CropAndPad¶
Crop/pad images by pixel amounts or fractions of image sizes.
Cropping removes pixels at the sides (i.e. extracts a subimage from a given full image). Padding adds pixels to the sides (e.g. black pixels).
Note
This augmenter automatically resizes images back to their original size
after it has augmented them. To deactivate this, add the
parameter keep_size=False.
API link: CropAndPad
Example. Crop or pad each side by up to 10 percent relative to its original size (negative values result in cropping, positive in padding):
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CropAndPad(percent=(-0.25, 0.25))

Example. Pad each side by 0 to 20 percent. This adds new pixels to the sides. These pixels will either be filled with a constant value (mode=constant) or filled with the value on the closest edge (mode=edge). If a constant value is used, it will be a random value between 0 and 128 (sampled per image).
aug = iaa.CropAndPad(
percent=(0, 0.2),
pad_mode=["constant", "edge"],
pad_cval=(0, 128)
)

Example. Pad the top side of each image by 0 to 30 pixels, the right side by 0-10px, bottom side by 0-30px and left side by 0-10px. Use any of the available modes to fill new pixels and if the mode is constant then use a constant value between 0 and 128.
aug = iaa.CropAndPad(
px=((0, 30), (0, 10), (0, 30), (0, 10)),
pad_mode=ia.ALL,
pad_cval=(0, 128)
)

Example. Crop/pad each side by up to 10px. The value will be sampled once per image and used for all sides (i.e. all sides gain/lose the same number of rows/colums).
aug = iaa.CropAndPad(
px=(-10, 10),
sample_independently=False
)

Pad¶
Pad images, i.e. adds columns/rows of pixels to them.
This is a shortcut for CropAndPad. It only accepts positive
pixel/percent values.
API link: Pad
Crop¶
Crop images, i.e. remove columns/rows of pixels at the sides of images.
This is a shortcut for CropAndPad. It only accepts positive
pixel/percent values and transfers them as negative values to CropAndPad.
API link: Crop
PadToFixedSize¶
Pad images to minimum width/height.
If images are already at the minimum width/height or are larger, they will not be padded. Note that this also means that images will not be cropped if they exceed the required width/height.
The augmenter randomly decides per image how to distribute the required
padding amounts over the image axis. E.g. if 2px have to be padded on the
left or right to reach the required width, the augmenter will sometimes
add 2px to the left and 0px to the right, sometimes add 2px to the right
and 0px to the left and sometimes add 1px to both sides. Set position
to center to prevent that.
API link: PadToFixedSize
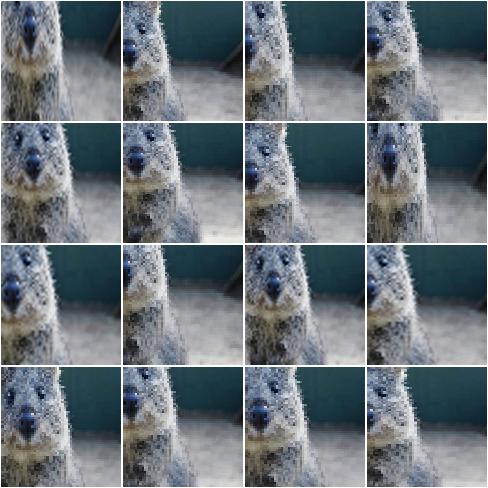
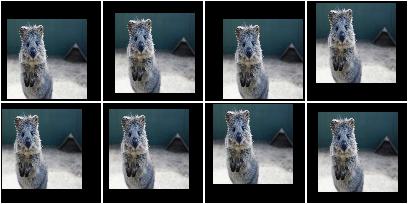
Example.
For image sides smaller than 100 pixels, pad to 100 pixels. Do
nothing for the other edges. The padding is randomly (uniformly)
distributed over the sides, so that e.g. sometimes most of the required
padding is applied to the left, sometimes to the right (analogous
top/bottom).
The input image here has a size of 80x80.
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.PadToFixedSize(width=100, height=100)
Example.
For image sides smaller than 100 pixels, pad to 100 pixels. Do
nothing for the other image sides. The padding is always equally
distributed over the left/right and top/bottom sides.
The input image here has a size of 80x80.
aug = iaa.PadToFixedSize(width=100, height=100, position="center")

Example.
For image sides smaller than 100 pixels, pad to 100 pixels and
use any possible padding mode for that. Do nothing for the other image
sides. The padding is always equally distributed over the left/right and
top/bottom sides.
The input image here has a size of 80x80.
aug = iaa.PadToFixedSize(width=100, height=100, pad_mode=ia.ALL)

Example.
Pad images smaller than 100x100 until they reach 100x100.
Analogously, crop images larger than 100x100 until they reach
100x100. The output images therefore have a fixed size of 100x100.
The input image here has a size of 80x120, so that the top/bottom sides
have to be cropped and the left/right sides have to be padded. Note that
the original image was resized to 80x120, leading to a bit of an
distorted appearance.
aug = iaa.Sequential([
iaa.PadToFixedSize(width=100, height=100),
iaa.CropToFixedSize(width=100, height=100)
])

CropToFixedSize¶
Crop images down to a fixed maximum width/height.
If images are already at the maximum width/height or are smaller, they will not be cropped. Note that this also means that images will not be padded if they are below the required width/height.
The augmenter randomly decides per image how to distribute the required
cropping amounts over the image axis. E.g. if 2px have to be cropped on
the left or right to reach the required width, the augmenter will
sometimes remove 2px from the left and 0px from the right, sometimes
remove 2px from the right and 0px from the left and sometimes remove 1px
from both sides. Set position to center to prevent that.
API link: CropToFixedSize
Example.
For image sides larger than 100 pixels, crop to 100 pixels. Do
nothing for the other sides. The cropping amounts are randomly (and
uniformly) distributed over the sides of the image.
The input image here has a size of 120x120.
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CropToFixedSize(width=100, height=100)

Example.
For sides larger than 100 pixels, crop to 100 pixels. Do nothing
for the other sides. The cropping amounts are always equally distributed
over the left/right sides of the image (and analogously for top/bottom).
The input image here has a size of 120x120.
aug = iaa.CropToFixedSize(width=100, height=100, position="center")

Example.
Pad images smaller than 100x100 until they reach 100x100.
Analogously, crop images larger than 100x100 until they reach
100x100. The output images therefore have a fixed size of 100x100.
The input image here has a size of 80x120, so that the top/bottom sides
have to be cropped and the left/right sides have to be padded. Note that
the original image was resized to 80x120, leading to a bit of an
distorted appearance.
aug = iaa.Sequential([
iaa.PadToFixedSize(width=100, height=100),
iaa.CropToFixedSize(width=100, height=100)
])

PadToMultiplesOf¶
Pad images until their height/width is a multiple of a value.
API link: PadToMultiplesOf
Example.
Create an augmenter that pads images to multiples of 10 along
the y-axis (i.e. 10, 20, 30, …) and to multiples of 6 along the
x-axis (i.e. 6, 12, 18, …).
The rows to be padded will be spread randomly over the top and bottom
sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.PadToMultiplesOf(height_multiple=10, width_multiple=6)
CropToMultiplesOf¶
Crop images down until their height/width is a multiple of a value.
Note
For a given axis size A and multiple M, if A is in the
interval [0 .. M], the axis will not be changed.
As a result, this augmenter can still produce axis sizes that are
not multiples of the given values.
API link: CropToMultiplesOf
Example.
Create an augmenter that crops images to multiples of 10 along
the y-axis (i.e. 10, 20, 30, …) and to multiples of 6 along the
x-axis (i.e. 6, 12, 18, …).
The rows to be cropped will be spread randomly over the top and bottom
sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CropToMultiplesOf(height_multiple=10, width_multiple=6)
CropToPowersOf¶
Crop images until their height/width is a power of a base.
This augmenter removes pixels from an axis with size S leading to the
new size S' until S' = B^E is fulfilled, where B is a
provided base (e.g. 2) and E is an exponent from the discrete
interval [1 .. inf).
Note
This augmenter does nothing for axes with size less than B^1 = B.
If you have images with S < B^1, it is recommended
to combine this augmenter with a padding augmenter that pads each
axis up to B.
API link: CropToPowersOf
Example.
Create an augmenter that crops each image down to powers of 3 along
the y-axis (i.e. 3, 9, 27, …) and powers of 2 along the x-axis (i.e.
2, 4, 8, 16, …).
The rows to be cropped will be spread randomly over the top and bottom
sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CropToPowersOf(height_base=3, width_base=2)
PadToPowersOf¶
Pad images until their height/width is a power of a base.
This augmenter adds pixels to an axis with size S leading to the
new size S' until S' = B^E is fulfilled, where B is a
provided base (e.g. 2) and E is an exponent from the discrete
interval [1 .. inf).
API link: PadToPowersOf
Example.
Create an augmenter that pads each image to powers of 3 along the
y-axis (i.e. 3, 9, 27, …) and powers of 2 along the x-axis (i.e. 2,
4, 8, 16, …).
The rows to be padded will be spread randomly over the top and bottom
sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.PadToPowersOf(height_base=3, width_base=2)
CropToAspectRatio¶
Crop images until their width/height matches an aspect ratio.
This augmenter removes either rows or columns until the image reaches
the desired aspect ratio given in width / height. The cropping
operation is stopped once the desired aspect ratio is reached or the image
side to crop reaches a size of 1. If any side of the image starts
with a size of 0, the image will not be changed.
API link: CropToAspectRatio
Example.
Create an augmenter that crops each image until its aspect ratio is as
close as possible to 2.0 (i.e. two times as many pixels along the
x-axis than the y-axis).
The rows to be cropped will be spread randomly over the top and bottom
sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CropToAspectRatio(2.0)
PadToAspectRatio¶
Pad images until their width/height matches an aspect ratio.
This augmenter adds either rows or columns until the image reaches
the desired aspect ratio given in width / height.
API link: PadToAspectRatio
Example.
Create an augmenter that pads each image until its aspect ratio is as
close as possible to 2.0 (i.e. two times as many pixels along the
x-axis than the y-axis).
The rows to be padded will be spread randomly over the top and bottom
sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.PadToAspectRatio(2.0)
CropToSquare¶
Crop images until their width and height are identical.
This is identical to imgaug.augmenters.size.CropToAspectRatio with
aspect_ratio=1.0.
Images with axis sizes of 0 will not be altered.
API link: CropToSquare
Example. Create an augmenter that crops each image until its square, i.e. height and width match. The rows to be cropped will be spread randomly over the top and bottom sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CropToSquare()
PadToSquare¶
Pad images until their height and width are identical.
This augmenter is identical to imgaug.augmenters.size.PadToAspectRatio
with aspect_ratio=1.0.
API link: PadToSquare
Example. Create an augmenter that pads each image until its square, i.e. height and width match. The rows to be padded will be spread randomly over the top and bottom sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.PadToSquare()
CenterPadToFixedSize¶
Pad images equally on all sides up to given minimum heights/widths.
This is an alias for imgaug.augmenters.size.PadToFixedSize with
position="center".
It spreads the pad amounts equally over all image sides, while
imgaug.augmenters.size.PadToFixedSize by defaults spreads them
randomly.
API link: CenterPadToFixedSize
Example.
Create an augmenter that pads images up to 20x30, with the padded
rows added equally on the top and bottom (analogous for the padded
columns).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CenterPadToFixedSize(height=20, width=30)
CenterCropToFixedSize¶
Take a crop from the center of each image.
This is an alias for imgaug.augmenters.size.CropToFixedSize with
position="center".
Note
If images already have a width and/or height below the provided width and/or height then this augmenter will do nothing for the respective axis. Hence, resulting images can be smaller than the provided axis sizes.
API link: CenterCropToFixedSize
Example.
Create an augmenter that takes 20x10 sized crops from the center of
images:
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
crop = iaa.CenterCropToFixedSize(height=20, width=10)
CenterCropToMultiplesOf¶
Crop images equally on all sides until H/W are multiples of given values.
This is the same as imgaug.augmenters.size.CropToMultiplesOf, but uses
position="center" by default, which spreads the crop amounts equally
over all image sides, while imgaug.augmenters.size.CropToMultiplesOf
by default spreads them randomly.
API link: CenterCropToMultiplesOf
Example.
Create an augmenter that crops images to multiples of 10 along
the y-axis (i.e. 10, 20, 30, …) and to multiples of 6 along the
x-axis (i.e. 6, 12, 18, …).
The rows to be cropped will be spread equally over the top and bottom
sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CenterCropToMultiplesOf(height_multiple=10, width_multiple=6)
CenterPadToMultiplesOf¶
Pad images equally on all sides until H/W are multiples of given values.
This is the same as imgaug.augmenters.size.PadToMultiplesOf, but uses
position="center" by default, which spreads the pad amounts equally
over all image sides, while imgaug.augmenters.size.PadToMultiplesOf
by default spreads them randomly.
API link: CenterPadToMultiplesOf
Example.
Create an augmenter that pads images to multiples of 10 along
the y-axis (i.e. 10, 20, 30, …) and to multiples of 6 along the
x-axis (i.e. 6, 12, 18, …).
The rows to be padded will be spread equally over the top and bottom
sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CenterPadToMultiplesOf(height_multiple=10, width_multiple=6)
CenterCropToPowersOf¶
Crop images equally on all sides until H/W is a power of a base.
This is the same as imgaug.augmenters.size.CropToPowersOf, but uses
position="center" by default, which spreads the crop amounts equally
over all image sides, while imgaug.augmenters.size.CropToPowersOf
by default spreads them randomly.
API link: CenterCropToPowersOf
Example.
Create an augmenter that crops each image down to powers of 3 along
the y-axis (i.e. 3, 9, 27, …) and powers of 2 along the x-axis (i.e.
2, 4, 8, 16, …).
The rows to be cropped will be spread equally over the top and bottom
sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CropToPowersOf(height_base=3, width_base=2)
CenterPadToPowersOf¶
Pad images equally on all sides until H/W is a power of a base.
This is the same as imgaug.augmenters.size.PadToPowersOf, but uses
position="center" by default, which spreads the pad amounts equally
over all image sides, while imgaug.augmenters.size.PadToPowersOf by
default spreads them randomly.
API link: CenterPadToPowersOf
Example.
Create an augmenter that pads each image to powers of 3 along the
y-axis (i.e. 3, 9, 27, …) and powers of 2 along the x-axis (i.e. 2,
4, 8, 16, …).
The rows to be padded will be spread equally over the top and bottom
sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CenterPadToPowersOf(height_base=3, width_base=2)
CenterCropToAspectRatio¶
Crop images equally on all sides until they reach an aspect ratio.
This is the same as imgaug.augmenters.size.CropToAspectRatio, but uses
position="center" by default, which spreads the crop amounts equally
over all image sides, while imgaug.augmenters.size.CropToAspectRatio
by default spreads them randomly.
API link: CenterCropToAspectRatio
Example.
Create an augmenter that crops each image until its aspect ratio is as
close as possible to 2.0 (i.e. two times as many pixels along the
x-axis than the y-axis).
The rows to be cropped will be spread equally over the top and bottom
sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CenterCropToAspectRatio(2.0)
CenterPadToAspectRatio¶
Pad images equally on all sides until H/W matches an aspect ratio.
This is the same as imgaug.augmenters.size.PadToAspectRatio, but uses
position="center" by default, which spreads the pad amounts equally
over all image sides, while imgaug.augmenters.size.PadToAspectRatio
by default spreads them randomly.
API link: CenterPadToAspectRatio
Example.
Create am augmenter that pads each image until its aspect ratio is as
close as possible to 2.0 (i.e. two times as many pixels along the
x-axis than the y-axis).
The rows to be padded will be spread equally over the top and bottom
sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.PadToAspectRatio(2.0)
CenterCropToSquare¶
Crop images equally on all sides until their height/width are identical.
In contrast to imgaug.augmenters.size.CropToSquare, this augmenter
always tries to spread the columns/rows to remove equally over both sides of
the respective axis to be cropped.
imgaug.augmenters.size.CropToAspectRatio by default spreads the
croppings randomly.
This augmenter is identical to imgaug.augmenters.size.CropToSquare
with position="center", and thereby the same as
imgaug.augmenters.size.CropToAspectRatio with
aspect_ratio=1.0, position="center".
Images with axis sizes of 0 will not be altered.
API link: CenterCropToSquare
Example. Create an augmenter that crops each image until its square, i.e. height and width match. The rows to be cropped will be spread equally over the top and bottom sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CenterCropToSquare()
CenterPadToSquare¶
Pad images equally on all sides until their height & width are identical.
This is the same as imgaug.augmenters.size.PadToSquare, but uses
position="center" by default, which spreads the pad amounts equally
over all image sides, while imgaug.augmenters.size.PadToSquare by
default spreads them randomly. This augmenter is thus also identical to
imgaug.augmenters.size.PadToAspectRatio with
aspect_ratio=1.0, position="center".
API link: CenterPadToSquare
Example. Create an augmenter that pads each image until its square, i.e. height and width match. The rows to be padded will be spread equally over the top and bottom sides (analogous for the left/right sides).
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.CenterPadToSquare()
KeepSizeByResize¶
Resize images back to their input sizes after applying child augmenters.
Combining this with e.g. a cropping augmenter as the child will lead to
images being resized back to the input size after the crop operation was
applied. Some augmenters have a keep_size argument that achieves the
same goal (if set to True), though this augmenter offers control over
the interpolation mode and which augmentables to resize (images, heatmaps,
segmentation maps).
API link: KeepSizeByResize
Example.
Apply random cropping to input images, then resize them back to their
original input sizes. The resizing is done using this augmenter instead
of the corresponding internal resizing operation in Crop.
import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
aug = iaa.KeepSizeByResize(
iaa.Crop((20, 40), keep_size=False)
)

Example. Same as in the previous example, but images are now always resized using nearest neighbour interpolation.
aug = iaa.KeepSizeByResize(
iaa.Crop((20, 40), keep_size=False),
interpolation="nearest"
)

Example. Similar to the previous example, but images are now sometimes resized using linear interpolation and sometimes using nearest neighbour interpolation. Heatmaps are resized using the same interpolation as was used for the corresponding image. Segmentation maps are not resized and will therefore remain at their size after cropping.
aug = iaa.KeepSizeByResize(
iaa.Crop((20, 40), keep_size=False),
interpolation=["nearest", "cubic"],
interpolation_heatmaps=iaa.KeepSizeByResize.SAME_AS_IMAGES,
interpolation_segmaps=iaa.KeepSizeByResize.NO_RESIZE
)
